What is the electronic configuration of potassium
What does the electronic configuration of potassium look like? In order to answer this question, let us consider the structure of the atom, as well as the rules for the distribution of electrons over levels and sublevels.
Quantum mechanics
The electronic configuration of potassium is describedSchrodinger equation. It connects the potential energy of the interaction of the nucleus and electrons, as well as the repulsion between particles having an equal charge. Quantum mechanics uses the postulates of this equation, explaining the existence of a certain energy reserve for each energy level.
Many-electron atoms
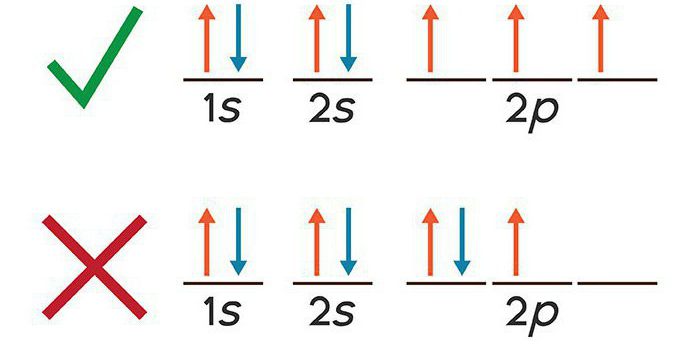
The electronic configuration of potassium is recorded withthe Pauli prohibition principle. Taking into account the peculiarities of the wave nature of electrons, he assumed that each negative particle is located on the "orbital", that is, it has a certain spatial existence. As for the many-electron atom, to which potassium belongs, no more than two electrons can be located on each orbital. As a result, four quantum numbers were identified, characterizing the state of the electron in the considered time interval.
The Klechkovsky rule
The electronic configuration of potassium is made up ofthe basis of the rule derived by Klechkovsky. Let's consider it in more detail. Depending on which orbital electrons are located, they have a certain amount of energy. First, there is a distribution of particles having a smaller energy reserve.
As the main energy characteristic for an electron is the principal quantum number corresponding to the period number.
In a multi-electron atom, not onlyattraction to the nucleus of electrons, but also repulsion between them. With an increase in the total spin of the particles, the energy of the electron shell decreases, and the number of electrons that have the same orientation of the eigenmoments of motion increases. A similar dependence in quantum chemistry is called the Hund rule.
Based on these two rules,electronic configuration of the potassium atom. Atomic spectra make it possible to determine the ground state of electrons, that is, to identify those particles that have a minimum energy reserve.
The essence of constructing an electronic formula for a multielectron potassium atom is quite simple: the electronic system must have a minimum energy, consistent with the Pauli exclusion principle.

Examples of the distribution of electrons over energy levels
Before considering what is electronicthe configuration of the potassium ion, we give simple examples. In the hydrogen atom, the nucleus contains one positive proton. Around the nucleus, one electron rotates in orbit. In the ground state the electronic formula of hydrogen has the following form: 1s. Let us consider the features of the spin orientation of this electron. According to the rule of Hund, he is co-directed with the back of the nucleus.
For helium, which has a second order number in the element table, two electrons are located on one orbital. Each of them has ½ spin, has a different direction of rotation.
Elements of the second energy level have two shells, each has its own supply of energy.
Potassium is an element of the fourth period of the system of elements, therefore it has four electronic levels, each of which contains different kinds of sublevels.
In the normal state, the atom of this alkali metal has the following configuration: 1s22s22p63s23p64s1.
The electronic configuration of the potassium ion has differencesfrom the atom. On the external energy level of the metal there is one valence electron. Since potassium shows reducing properties, during interactions with other atoms it gives a valence electron, turns into a positive ion (cation), which has the following electronic configuration: 1s22s22p63s23p64s0.

Conclusion
For each chemical element,located in the periodic table, you can make electronic configurations, armed with the Hund rule, the Pauli prohibition principle, and the Klechkovsky formula. In addition to the electronic configurations of atoms in inorganic chemistry, the formulas of cations and anions formed as a result of chemical interactions also form.








