Metric thread: dimensions. Metric thread: GOST
It is well known that threaded is one of the mostcommon detachable joints, allowing to perform assembly and disassembly work without damage to the integrity of structures, machines and mechanisms. The basis of this connection is the thread applied on two or more surfaces of the bodies of rotation, which is basically divided according to the indicators described below. The classification of threads is presented in the table below.

Thread metric
Screw threading on or in a material havingprofile of the tooth in the form of an isosceles triangle, is a metric thread, its dimensions are measured in millimeters. According to the shape of the application surface, this thread is cylindrical, but can be conical.

The latter is most popular in use, especially for the following fasteners:
- bolts;
- Anchors;
- screws;
- hardware;
- hairpins;
- nuts and stuff.

Screw thread applied to the conical baseform, is called a metric taper thread. It is used in places requiring fast locking of joints, without additional sealing and with the termination of leakage by simple pulling along the axis. Used for the installation of plugs and pipe connections:
- oil;
- oil;
- gas;
- water;
- air.
It is important to know that the conical andcylindrical threads have the same profile, which allows to screw them together. Metric threads are classified by size, direction of rotation, step and additional parameters, which are reflected in the marking.
Metric thread sizes
The spread of the diameters of this thread inThe industry has a range from 0.25 to 600 mm, with a diameter of more than 68 mm, the thread will be only shallow, whereas up to this value it will vary. Thread with a large step is used in joints under large and shock loads. It is also interesting that at a large thread the pitch is always fixed in relation to the diameter, in contrast to the small one, which can vary, which is separately and additionally indicated in the marking.
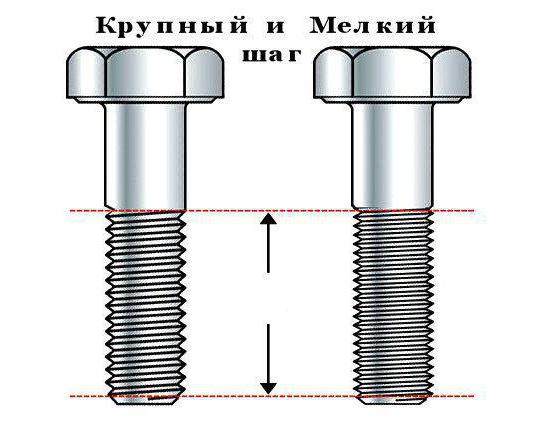
For example, if in technical documents ordrawings in the places of connection of parts meets "M16", this means that the letter M means metric thread. The dimensions of the outer diameter of the coils are 16 mm, and the large pitch of the standard thread is 2 mm, according to the information in the table (the thread of the second row is shown in parentheses). So, the thread is metric: the main dimensions (GOST 24705-2004).
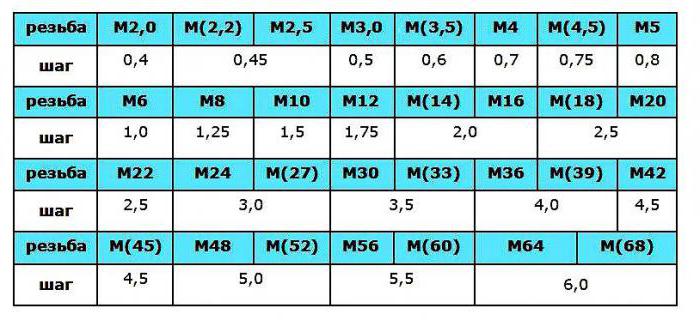
Fine thread threads
In marking the small step is indicated afterdiameter. It looks like this: “M16 × 0.5”, where, as already known, M is a metric thread. The dimensions of the outer diameter are 16 mm, with a step size of 0.5 mm. Interestingly, after a diameter of 2 mm, the difference between the thread pitch becomes significantly noticeable, leading to separation. Moreover, products of equal diameter have several types of fine thread pitch, like those of 16 mm:
- 1.5 mm;
- 1.0 mm;
- 0,75 mm;
- 0.5 mm.
As an example, a part of the table is given, which makes it possible to understand and visually assess the range of small threads, without taking the major step discussed earlier.
Metric thread: main dimensions (GOST 24705-2004)

Specified Parameters
In multiple threads, the pitch is indicated separately (in parentheses), and in its place the number of entries is indicated. Here's how this and other additional parameters are indicated when marking:
- (P1) - where P is a step of 1 mm, and turns - 3 (example: M42 × 3 (P1));
- LH - left-hand thread (example: M40 × 2LH);
- MK - metric thread conic (example: MK24x1, 5);
- EG-M or GM, where G denotes a thread on a cylindrical base of a wire insert or fitting (example: EPL 6-GM5);
- g, h, H - tolerance field, is the average tolerancediameter in combination with the diameter of the protrusion (example: M12-6g), and with different tolerances of internal and external diameters in the marking both tolerances are indicated (example: M12-6g / 8H).

Thread diameters
There are indicators that are indicated in the summary tables, which are important to consider in cases when the metric thread is considered - dimensions diameters:
- external (D and d);
- internal (D1 and d1);
- medium (D2 and d2);
- inner along the bottom of the depression (d3).
With widespread use in a slide-fit threaded joint, the average diameter has become more important, and in cases of equality of values, d2 bolt and smallest d2 nuts.
Capital letters D denote the numbers.diameters of internal threads, and parts applied to the external surface are denoted by small letters - d. Numbers indicate location. The degree of accuracy of tolerance fields is classified by letter characters: E, F, G, H, d, e, f, g, h, and, as in diameters, the size is indicated by the location.
Ratio of metric and inch threads
In contrast to European countries and countries close to them,where, after the reign of Napoleon, the metric system became widespread, in the countries of the former colonies of Britain and its satellites all measurements occur in the imperial system. In this system, the measurement of threads and their connections are made in inches.
Screw thread having a tooth profile in the forman isosceles triangle, with a vertex angle of 55 degrees. (in the UTS-standard for the USA and Canada - 60 degrees), is called inch thread, its dimensions are set in inches, and the pitch is in the number of turns per inch (1 "= 24.5 mm). Such fastening threads are made in from 3/16 ", with the designation indicated only the outer diameter.

Sizes of inch and metric threads are measured with a caliper and ifa metric thread of this will be sufficient, then a special table is used in inch measurement. When measuring threads, special templates are used, but there is also a popular method for measuring a pitch: if, wrapping a thread with a sheet of paper, you scroll the product several times, a mark is printed on the paper, allowing you to measure with a ruler. When using a tetrad sheet as a paper in a cell, there is no need for a ruler - it is enough to count the number of marks in 2 cells (1 cm) and divide by 10.

Hole sizes
Getting the thread is due to:
- cold rolling rollers and heads;
- cutting with chisels, combs or cutters;
- cutting dies or taps;
- precision casting;
- abrasive or EDM machining.

For cutting external threads, the workpiece is attachedcylindrical shape and chamfered, and for the inner drill a little smaller than the required metric thread (dimensions) hole, but larger than its internal diameter. After all, when determining the dimensions of the holes for a metric thread, it is necessary to take into account that when cutting a notch inside, a partial extrusion of material occurs, which subsequently participates in the formation of a threaded profile. It is also important to reckon with the properties of the material in which drilling is performed, reducing the size of the drill by 0.1 mm.
Dimensions of nuts with metric thread
Nut - one of the components of the mountingelements with internal thread. They differ in height with respect to diameter and strength, by purpose and configuration. Turnkey or hexagon nuts are the most widely used, here is a list of them indicating the State Standards:
- GOST 5915-70 - medium size;
- GOST 15523-70 - high;
- GOST 22354-77 - increased strength;
- GOST 5916-70 - low nut with a recess;
- GOST 10605-94 - under the thread diameter of more than 48 mm.

There are many nuts and special purpose, here are some examples and their guests:
- cap type (hexagonal) - GOST 11860-85;
- for manual screwing (wing nuts) - GOST 3032-74;
- slotted crown - GOST 5919-73;
- rounded with slotted - GOST 11871-88, GOST 10657-80;
- round, with end, radial holes - GOST 6393-73;
- for rigging work (eye nuts) - GOST 22355 (DIN580, DIN 582).
The most important parameter of connections with thread is the matching nuts and thread. Values of more popular threads with a large pitch are shown in the table below, where S is the turnkey size, e - the width of the nut, and m its height.
Table of conformity of threads and nuts (GOST 5915-70 and GOST 10605-94)

Standards
The main carving sizes submit to GOST24705-2004, which modifies the standard - ISO 724: 1993 (international classification). Since July 1, 2005, this GOST is the state standard of the Russian Federation and takes into account the interests of the economy of another 12 countries that were previously part of the USSR and voted for it. The dimensions of metric threads of GOST 9150 of wide use, as well as diameters and steps of GOST 8724 fall under its action.
According to the norms of interchangeability, this GOST refers to the following international and national standards systems:
- GOST 8724-2002 (ISO 261-1998);
- GOST 9150-2002 (ISO 68-1: 1998);
- GOST 11708-82;
- GOST 16093—2004 (ISO 965-1: 1998 and ISO 965-3: 1998).
This GOST fixes all basic dimensions, possible tolerances, terminology and formulas for calculating diameters:
- D2 = D - 2 x 3/8 H = D - 0.6495 P;
- d2 = d - 2 x 3/8 H = d - 0.6495 P;
- D1 = D - 2 x 5/8 H = D - 1.0825 P;
- d1 = d - 2 x 5/8 H = d - 1.0825 P;
- d3 = d - 2 17/24 H = d - 1.2267 P.
It's hard to imagine modern life withoutmachines and mechanisms, it is even harder to imagine a technique without detachable connections, which provides a thread. Efficiency, relative ease of manufacture and comfortable use of threaded connections provided an honorable place in world history.









